PYC-003
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is a severe disease that leads to kidney failure
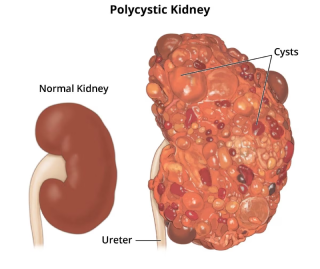
ADPKD is caused by insufficient expression of one gene (PKD1) in the renal tubular epithelial cells of the kidney
Unaffected
|
ADPKD
|
Genetic mechanism underlying disease pathology |
|
|---|---|---|---|

|

|
PKD1 DNA |
80% of ADPKD cases are caused by mutations in one copy of the PKD1 gene1 |

|

|
PKD1 RNA |
The mutation leads to an unstable RNA message that is rapidly degraded |
|
|
|
PC1
|
This leads to renal tubule epithelial cells of the kidney having half as much PC1 protein as they require to function normally – this protein is the rate-limiting modulator of cystic disease4 |

|

|
||

|

|
||

|
|
Kidney
|
Driving the formation of fluid filled cysts, ultimately leading to destruction of kidney function & architecture |
PYC-003 is designed to increase PC1 expression to address the root cause of ADPKD
Unaffected
individual
-
PKD1 DNA



-
PKD1 RNA




-
PC1 Protein

Functional PC1 expression = 100%
2 ‘healthy’ copies of PKD1 results in functional PC1 protein expression
ADPKD patient treated
with PYC-003
-
PKD1 DNA




-
PKD1 RNA




-
PC1 Protein

Restoration of PC1 expression towards 100%
PYC-003 increases expression of the remaining healthy copy of PKD1 RNA to compensate for the PC1 protein insufficiency and reverse cyst formation
Treatment with PYC-003 results in decreased frequency and area of cysts in a 3D model of PKD derived from patients with late-stage disease
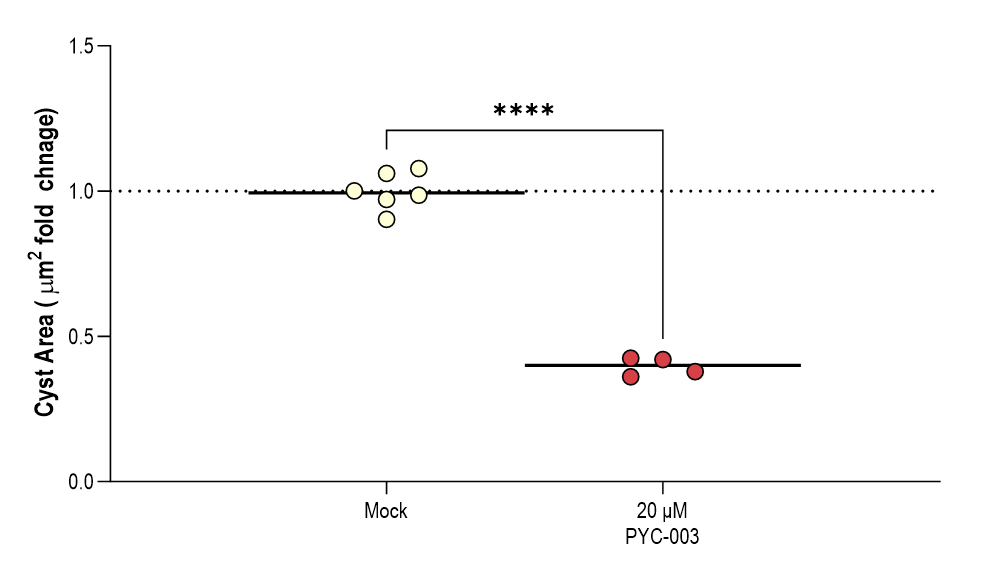
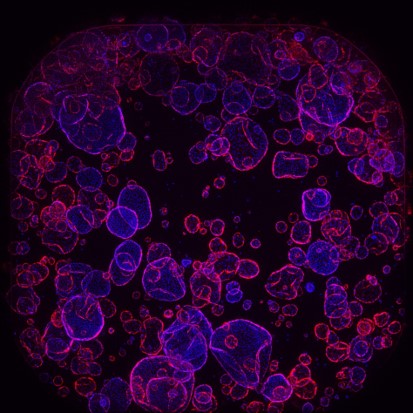

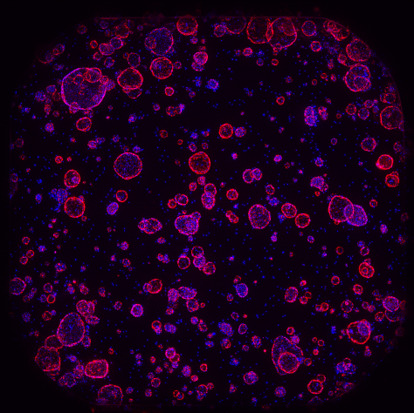
Treatment with PYC-003 results in decreased frequency and area of cysts in a 3D model of PKD derived from patients with late-stage disease. Images captured 7 days after treatment. Mock control samples treated with 5% H2O. Data are presented as mean+S.D (N=1 biological replicate with 4-6 technical replicates). Statistical significance was analyzed using Student’s t-test. *p=0.05, **p=0.01, ***p=0.005, ****p0.0001 . See https://www.crownbio.com/hubfs/WRCrownbio2021%20Assets/Resources/FactSheet/Crown-Bioscience-Factsheet-Cyst-Swelling-Assay-for-ADPKD.pdf for details of model and ASX release of 13 November 2023.
